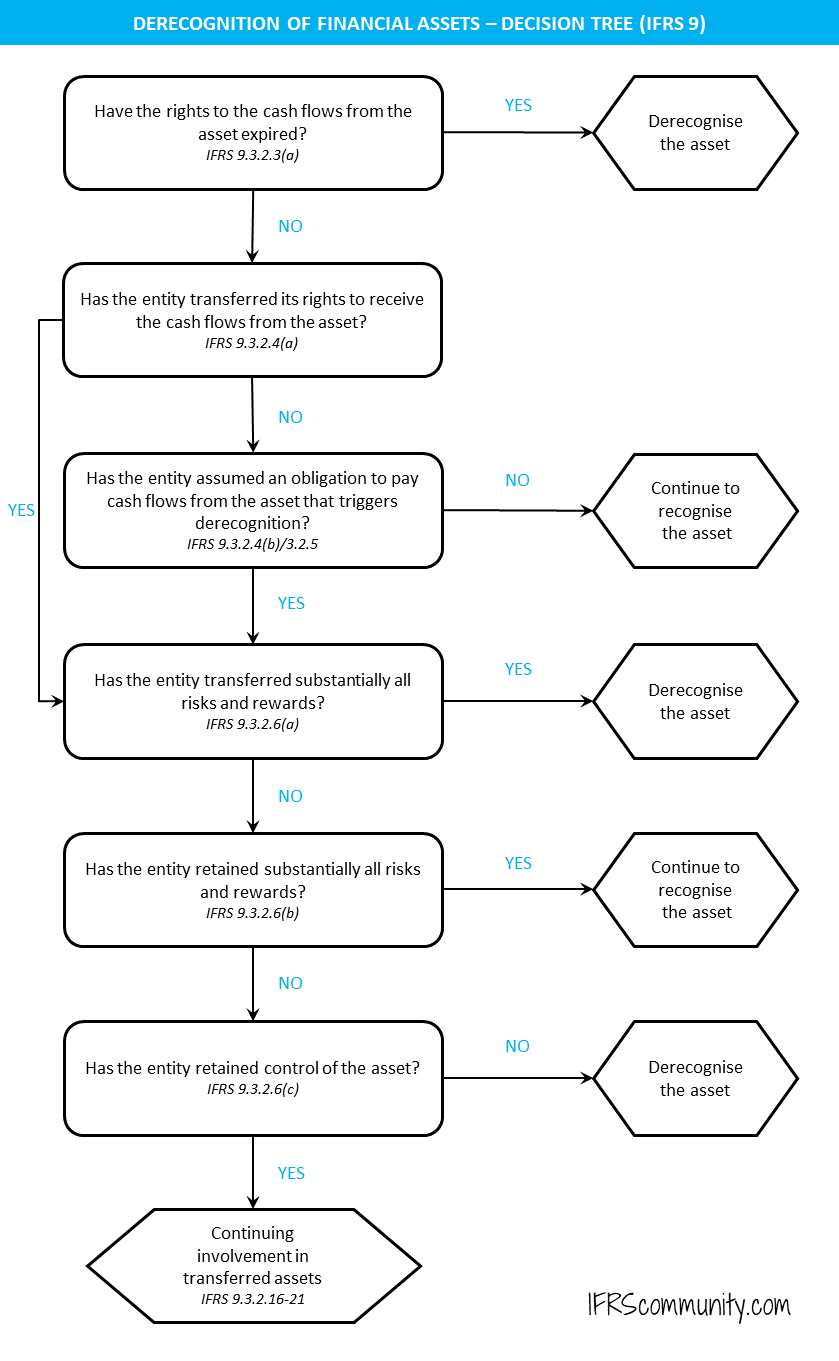
Supreme Info About Ifrs 9 Fair Value Through Profit And Loss

It determines whether cash flows will.
Ifrs 9 fair value through profit and loss. Carrying amount is the amount at which an asset is recognised in the statement of financial position. Financial liabilities at amortized cost; Total revenue reaches $9.8 million in quarter four, an increase of 35% year over year.
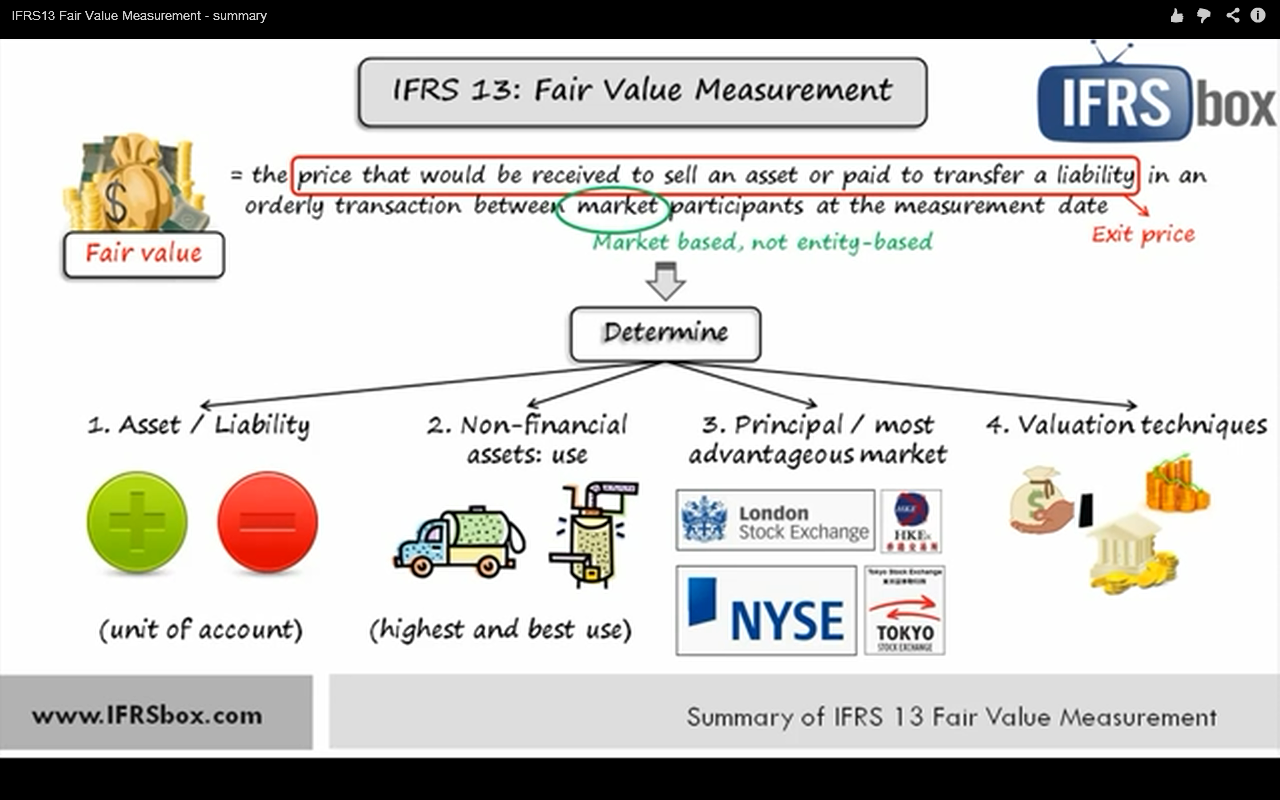
Assets and liabilities measured at fair value through profit or loss (‘fvtpl’) as the name suggests, assets or liabilities at fvtpl are subsequently. Under ifrs 9 all financial instruments are initially measured at fair value plus or minus, in the case of a financial asset or financial liability not at fair value through profit or loss,. Non‑monetary items that are measured at fair value [refer:
Ifrs 9 is effective for annual periods beginning on or after 1 january 2018 with early application permitted. The amount of change in fair value attributable to changes in. Whilst there is a fair value option to fair value through profit or loss (fvtpl) that can be elected, for entities to classify and measure at amortised.
And − the fair value gain or loss that would have been recognised in profit or loss or oci during the reporting. And financial liabilities at fair value through profit or loss; Saas revenue growth of 58% drives gross margin to 72% in quarter four.
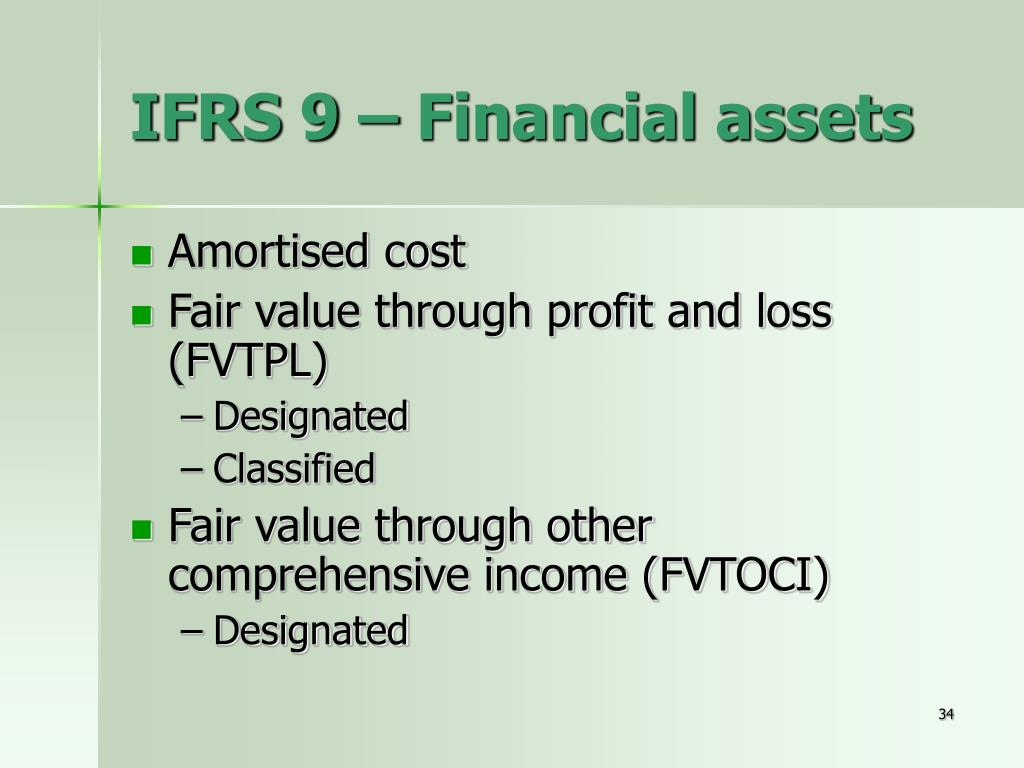
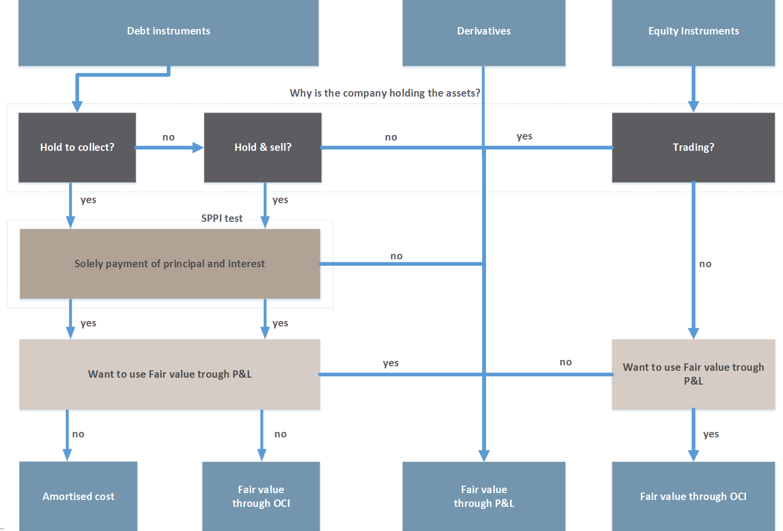
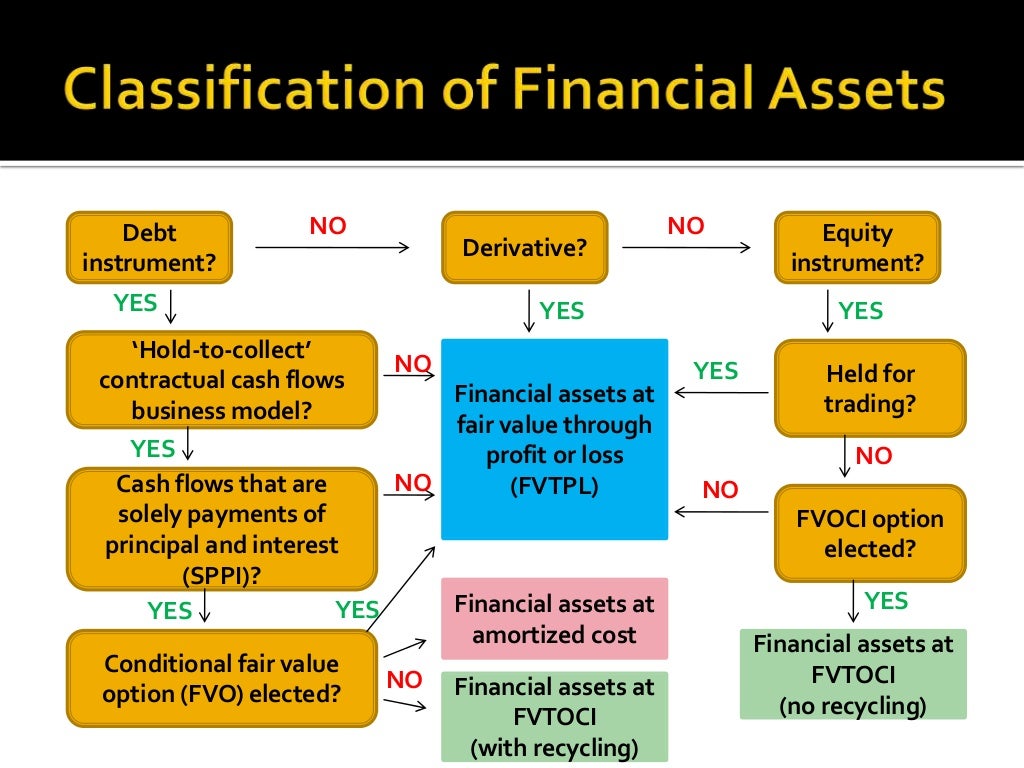
6.7 option to designate a credit exposure as measured at fair value through profit. Ifrs 9 has three classification categories for debt instruments: The default category is fair value through profit or loss (fvpl).
June dec interim reports annual report 31 dec 2018 overview of ifrs 9 classification and measurement technical considerations business model assessment (held to collect/sell). May 4, 2020 ifrs 9 requires changes in fair value on financial liabilities designated as at fvtpl to be split into: Instruments will be classified either at amortised cost, the newly established measurement category fair value through other comprehensive income (fvoci) or fair value.
Ifrs 9 specifies how an entity should classify and measure. Profit/(loss) for the period 11 (391) (485) (1,740) items that will not be reclassified to profit or loss: According to ifrs 9, a company’s business model refers to how an entity manages its financial assets in order to generate cash flows.
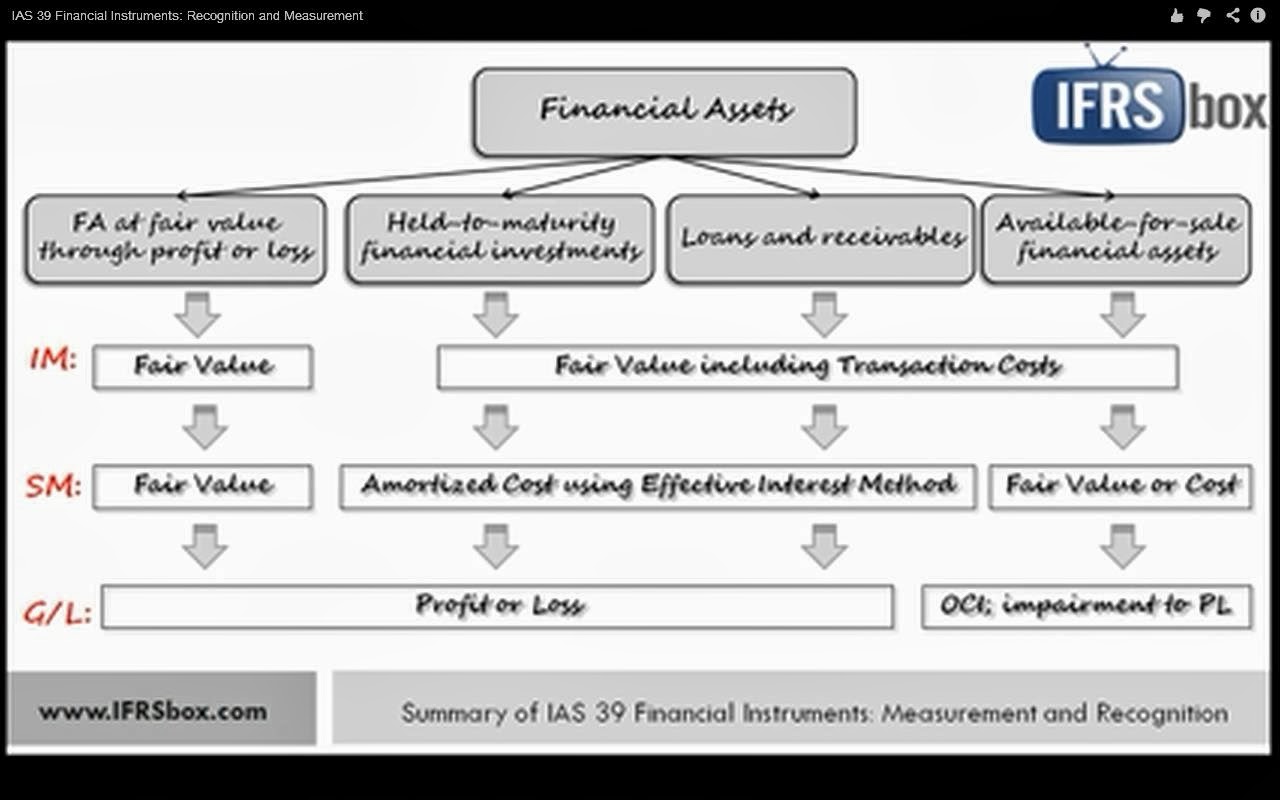
Of exchange differences recognised in profit or loss except for those arising on financial instruments. Zloans and receivables and held to maturity financial assets are measured at amortised cost. Under ifrs 9 all financial instruments are initially measured at fair value plus or minus, in the case of a financial asset or financial liability not at fair value through profit or loss,.
Fair value through profit or loss (fvpl) fvpl is the default treatment for equity. The following terms are used in this standard with the meanings specified: Fair value through profit or loss—any financial assets that are not held in one of the two business models mentioned are measured at fair value through profit or loss.
Under the ifrs 9 ‘expected loss’ model, a credit. Fair value through profit and loss (fvpl) is the residual category as per ifrs 9, and the objective is to establish principles for the financial reporting of financial assets. According to ifrs 9, a company’s business model refers to how an entity manages its financial assets in order to generate cash flows.