Supreme Tips About Dividends Declared On Balance Sheet
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/FacebookbalancesheetREDec2018-5c73549b46e0fb00014ef630.jpg)
When a corporation's board of directors declares a cash dividend on its stock, the following will occur:
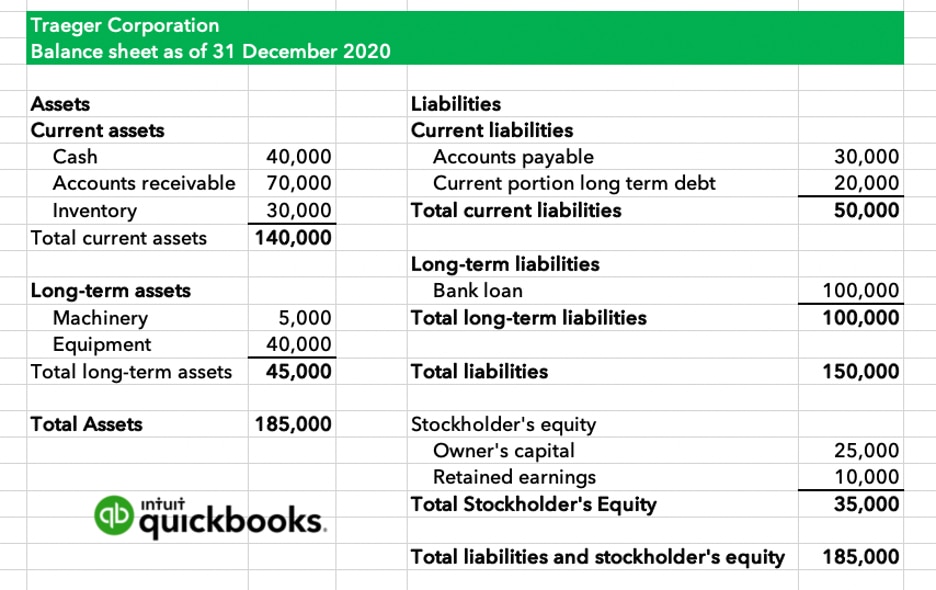
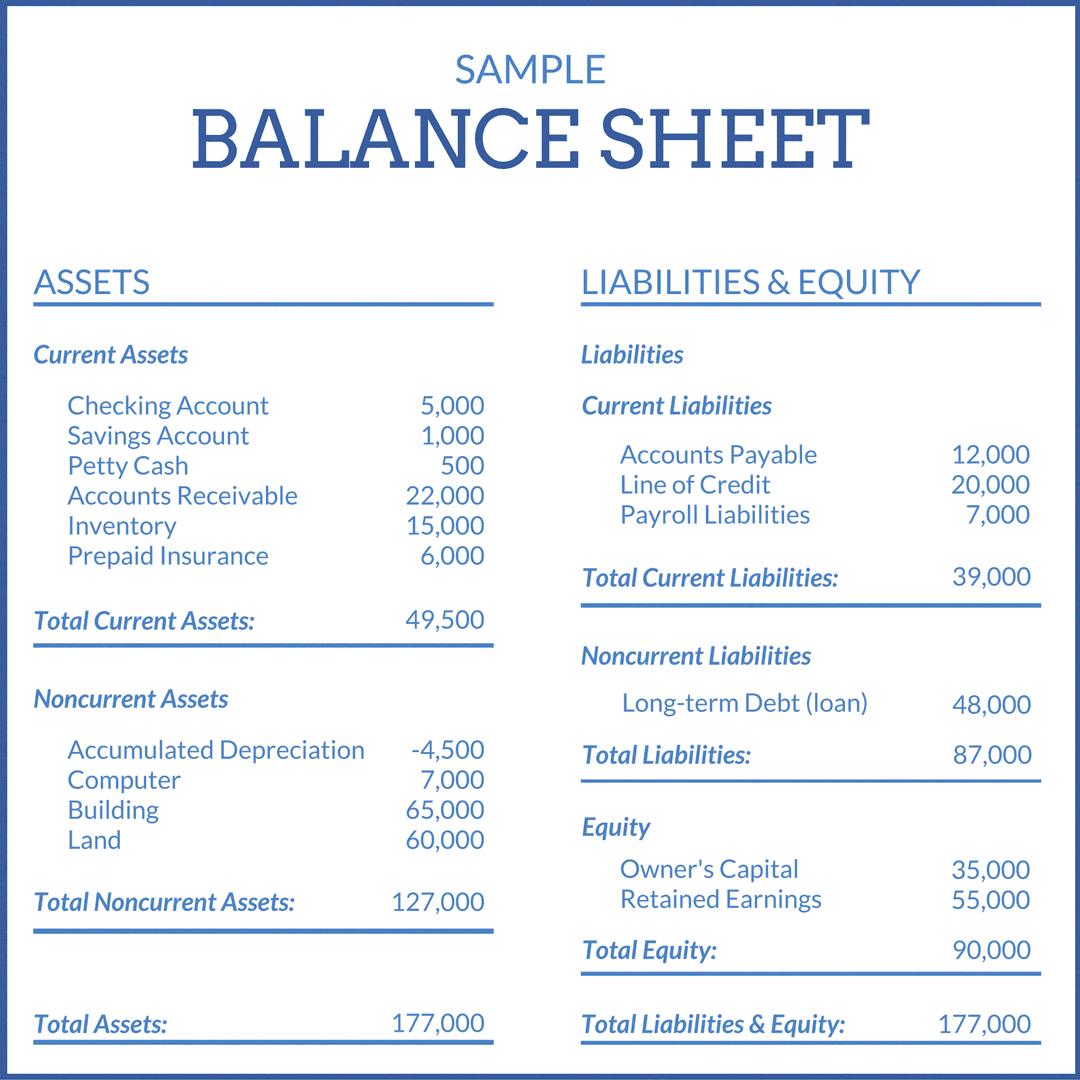
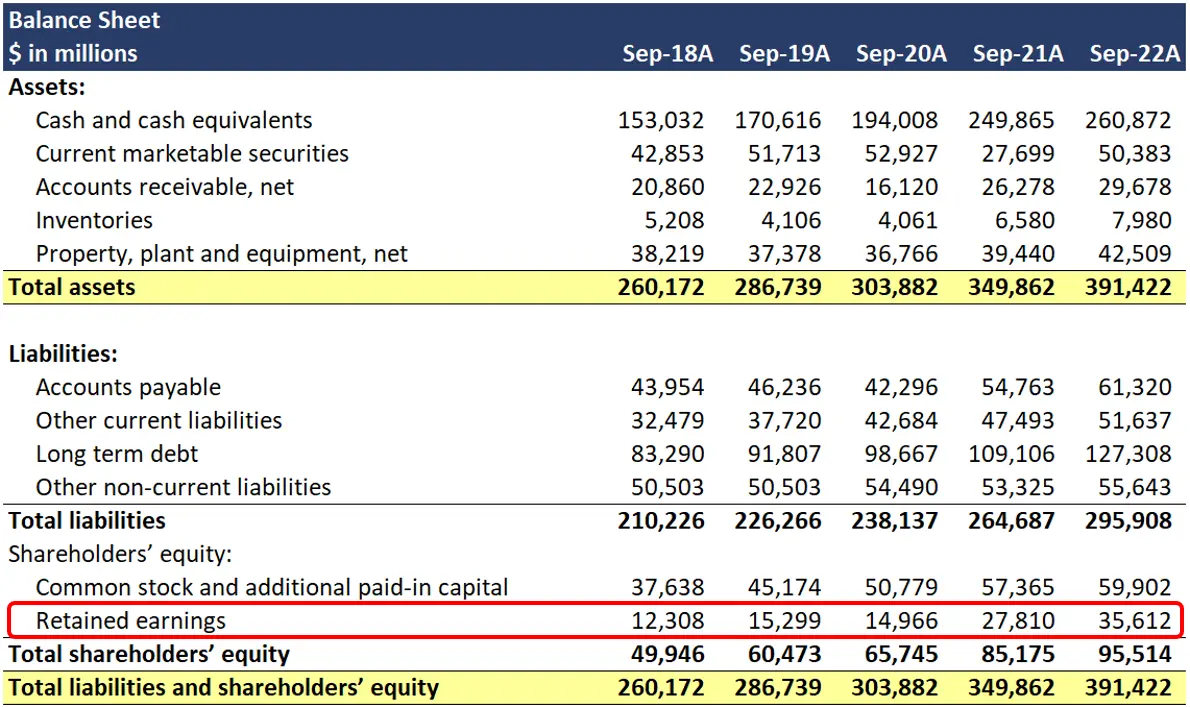
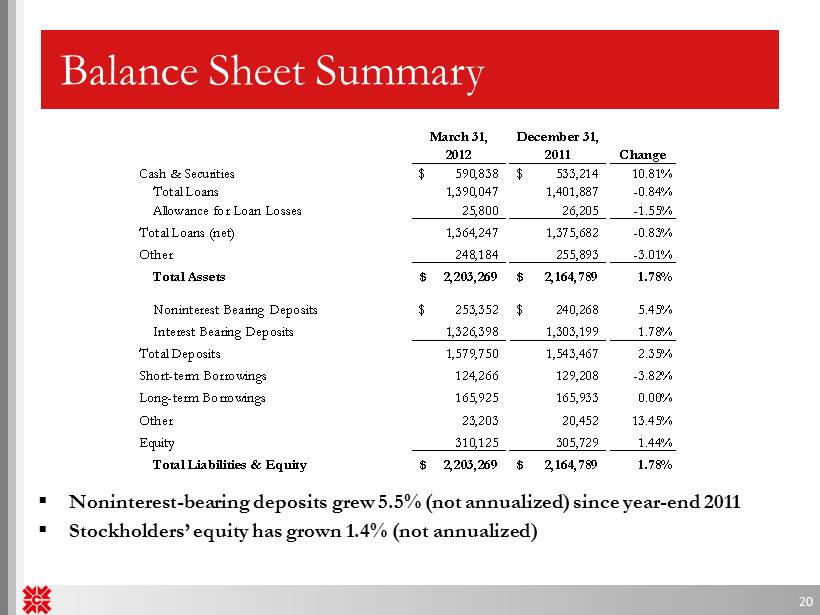
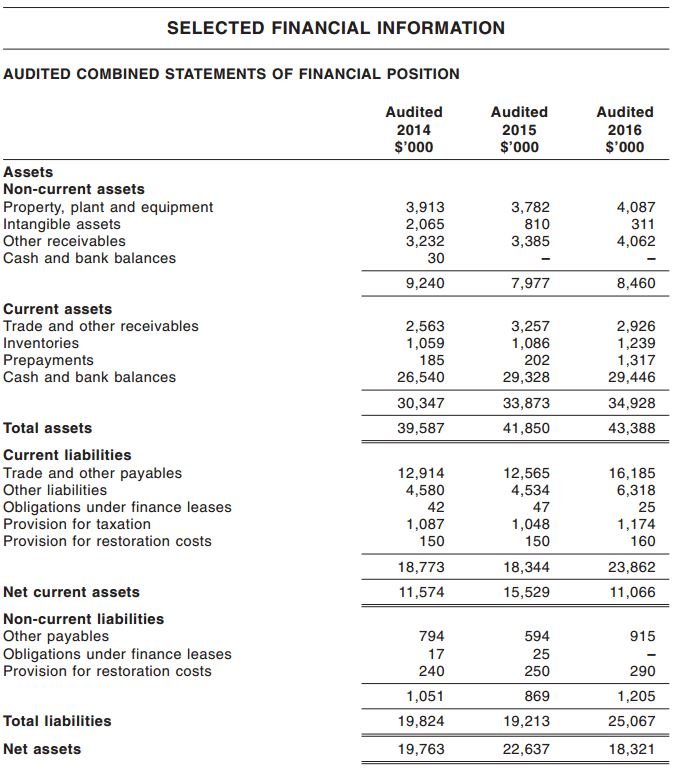
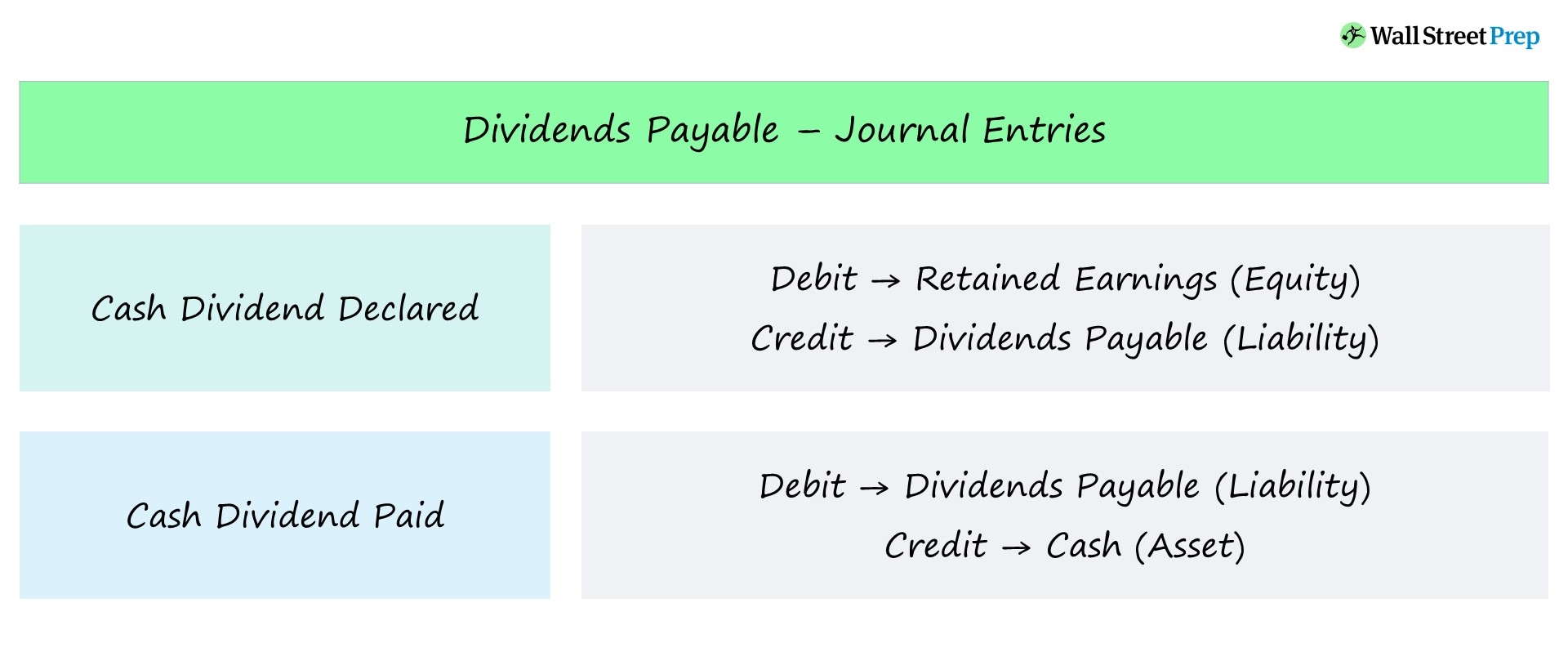
Dividends declared on balance sheet. Retained earnings (a part of stockholders' equity) will decrease; Recall that dividends reduce retained earnings which is summarised and reported in the retained earnings column of the balance sheet. It reduces earnings and creates a “dividends payable” liability.
(many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Dividends paid to natural persons are net, the company must account for gross dividends and with holdings to be paid to the tax authorities. The dividends payable account appears as a current liability on the balance sheet.
Distribution of assets, also called property dividends, will. Cash dividends affect two areas on the balance sheet: When cash dividends are paid, this reduces the cash balance stated within the assets section of the balance sheet, as well as the offsetting amount of retained earnings in the equity section of the report.
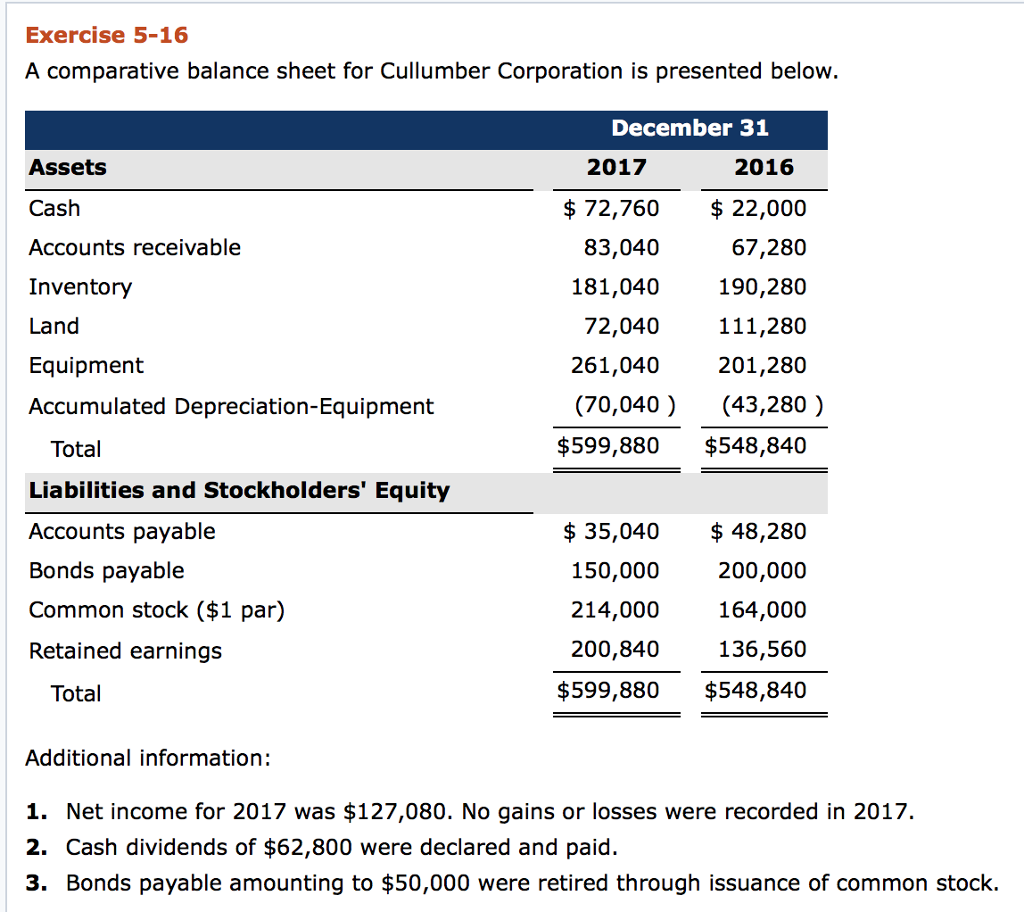
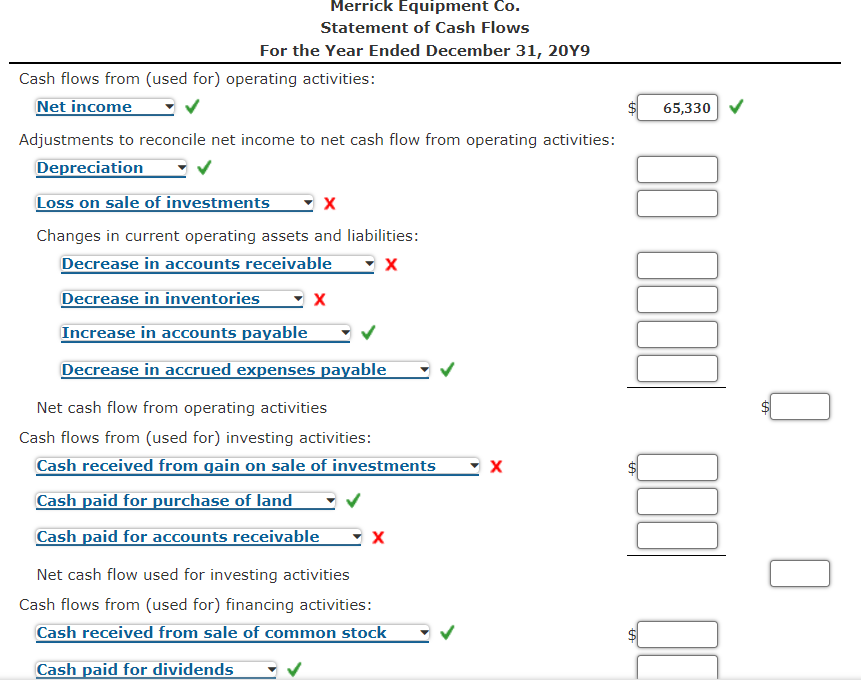
Dividends declared during the year are reported on the (1) statement of changes in equity and (2) balance sheet. Examples of how cash dividends affect the financial statements. When a stock dividend has been declared, but not issued at the balance sheet date, the sum of the number of shares declared as a stock dividend and the total number of shares outstanding should usually be disclosed on the face of the balance sheet.
Dividends payable is classified as a current liability on the balance sheet, since the expense represents declared payments to shareholders that are generally fulfilled within one year. When the dividends are paid, the effect on the balance sheet is a decrease in the company's retained earnings and its cash balance. When a stock dividend is declared, the amount to be debited is calculated by multiplying the current stock price by shares outstanding by the dividend percentage.
Once the dividends are paid to the shareholders, the liability is reduced, reflecting the distribution of dividends. Investors will not find a separate balance sheet account for dividends that have been. Dividends that were declared but not yet paid are reported on the balance sheet under the heading current liabilities.
Accounting principles ii dividends dividends the board of directors must authorize all dividends. Gain insights into how this key financial indicator impacts a company's financial health. Dividends declared are recorded in the accounting records as a liability of the corporation.
Cash dividends are the most popular type of dividend payment. By the time a company's financial statements have been released, the dividend would have already been paid and the. In terms of classification, dividends declared but not yet paid are reported as a current liability in the liabilities section of the balance sheet under “dividends payable.”.
A “dividend declared” is when the board of directors announces dividend distribution. The company may distribute dividends after emergency funds are met, boosting market confidence without losing money. Dividends on common stock are not reported on the income statement since they are not expenses.
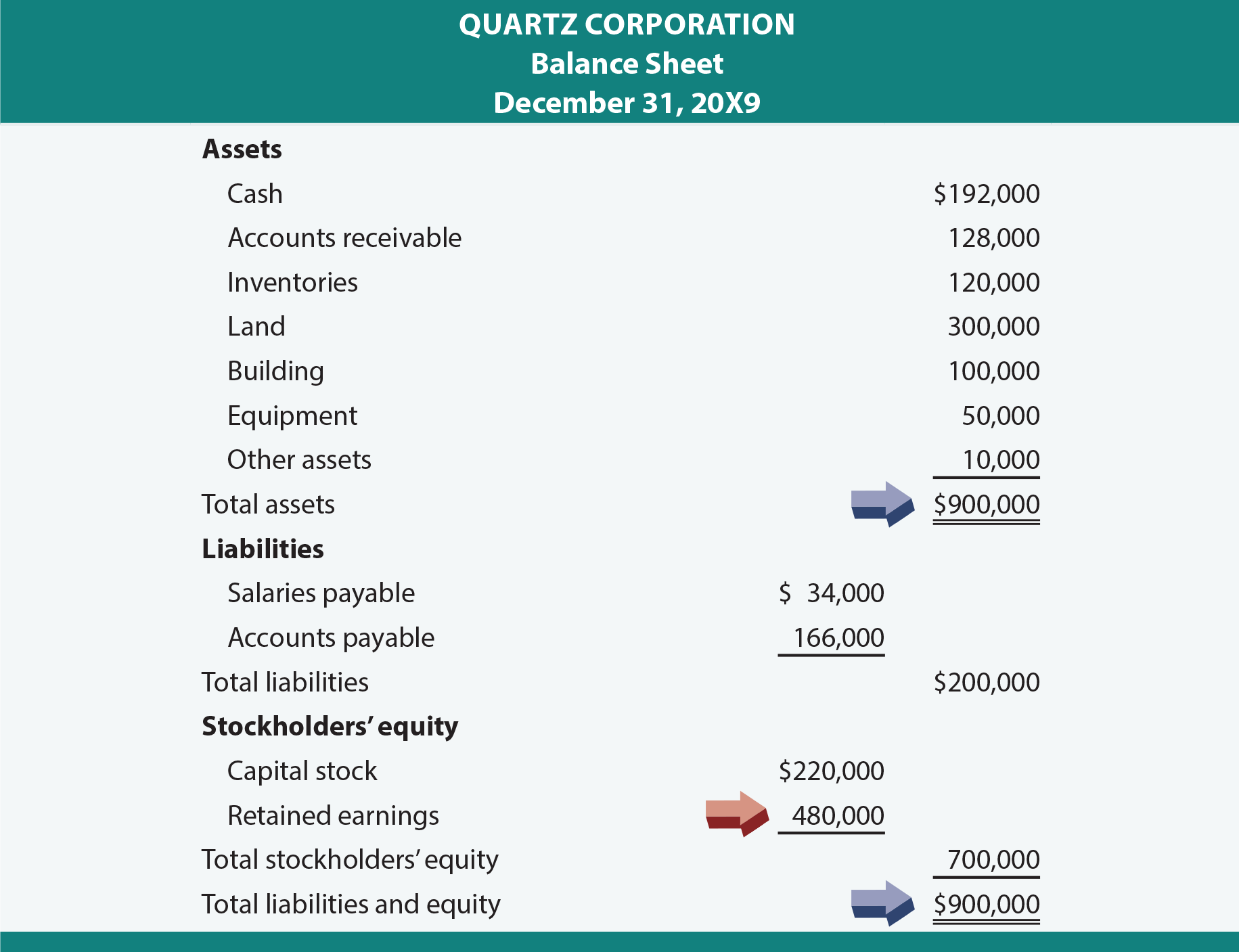
When the board of directors makes such a decision and declares a dividend for payment to stockholders, the retained earnings account on the company's balance sheet is reduced by the amount of the. To illustrate the entries for cash dividends, consider the following example. Dividends in the balance sheet.